Empty
Empty
Empty
CFrame (Coordinate Frame) is a data type in Roblox that represents the position and orientation of objects in 3D space. By understanding how to create and manipulate CFrames, you can achieve precise control over the placement and rotation of parts and models in your games.
| Position | The location of the object in the 3D world. |
| Orientation | The rotation of the object in the 3D world. |
CFrame Example
Empty
Empty
Empty
local myCFrame = CFrame.new(10, 5, -3)Empty
Empty
Empty
local part = script.Parent
part.Position = Vector3.new(0, 5, 0)
-- Move the part to a new position using CFrame
part.CFrame = CFrame.new(10, 5, -10)Roblox Studio
Empty
Empty
Empty
local part = script.Parent
part.Position = Vector3.new(0, 0.5, 0)
-- Rotate the part 45 degrees around the Y-axis
part.CFrame = CFrame.new(0, 0.5, 0) * CFrame.Angles(0, math.rad(45), 0)Roblox Studio
Empty
Empty
Empty
local part = script.Parent
part.Position = Vector3.new(0, 0.5, 0)
-- Move the part to (10, 5, -3) and rotate it 45 degrees around the Y-axis
part.CFrame = CFrame.new(10, 5, -3) * CFrame.Angles(0, math.rad(45), 0)Roblox Studio
Empty
Empty
Empty
local part = script.Parent
part.Position = Vector3.new(0, 2.5, 0)
-- Make the part look at the point (10, 2.5, -3)
local targetPosition = Vector3.new(10, 2.5, -3)
part.CFrame = CFrame.new(part.Position, targetPosition)Roblox Studio
CFrame (World Space vs Object Space)
World Space
WorldSpace refers to the global coordinate system of the game world.
Empty
Empty
Empty
- A point's position is defined relative to a fixed origin of the world.
- A point's position is defined relative to a fixed origin of the world.
- Transformations (like translations, rotations, and scaling) are applied relative to the world's origin.
- Coordinates in WorldSpace are absolute, meaning they are not affected by the position or orientation of any parent or other objects.
Object Space
ObjectSpace, also known as local space, refers to the coordinate system that is relative to an object.
Empty
Empty
Empty
- A point's position is defined relative to the object's origin (not the world origin).
- A point's position is defined relative to the object's origin (not the world origin).
- Transformations are applied relative to the object’s own axes, which may be rotated and scaled compared to the world axes.
- This is particularly useful when dealing with child objects in a hierarchy, as their transformations are based on the position, orientation, and scale of their parent object.
Empty
Empty
Empty
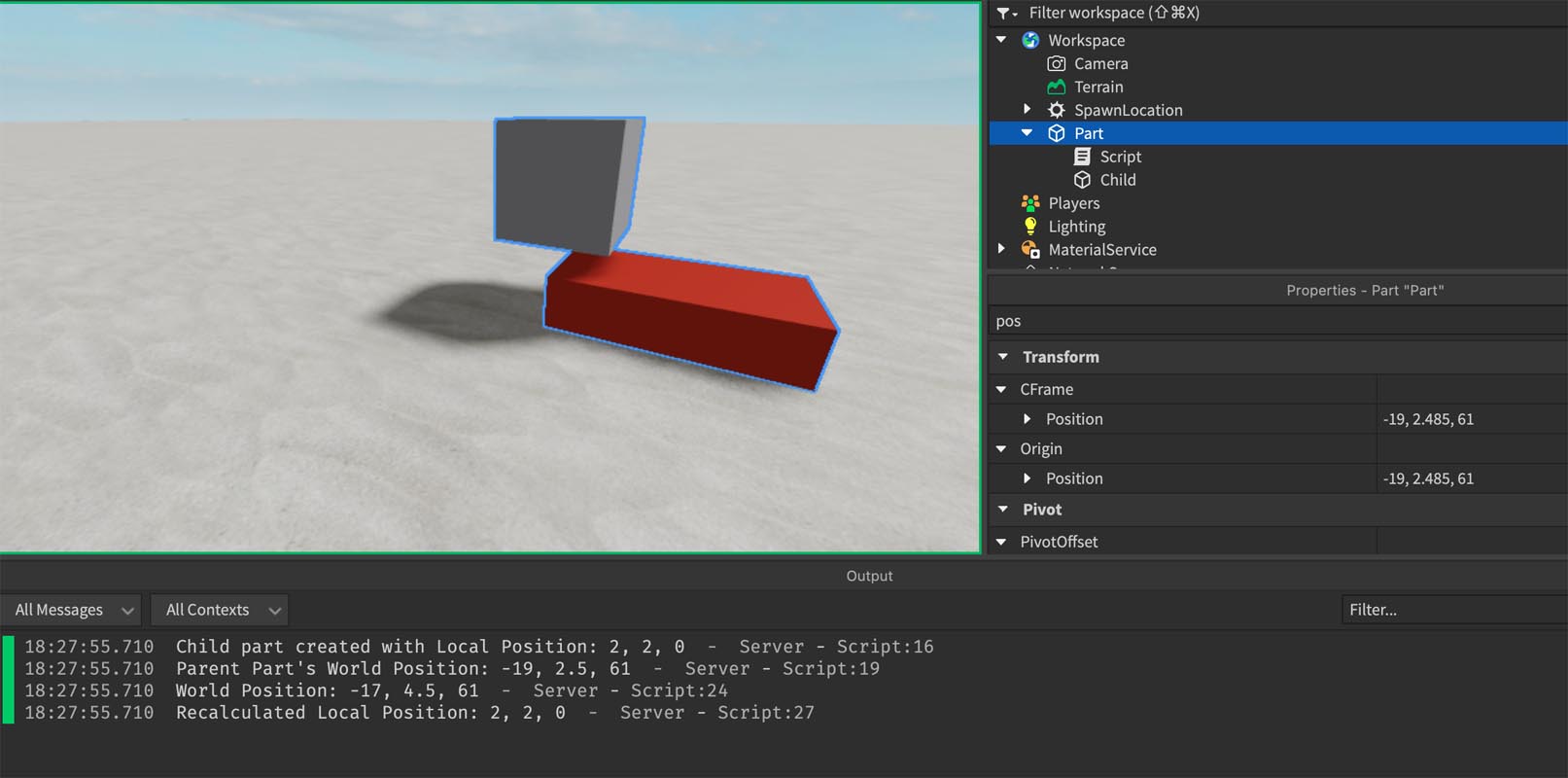
-- Get a reference to the parent part
local parentPart = script.Parent
-- Function to create a child part and set its position using local CFrame
local function createChildPart()
-- Create the child part
local childPart = Instance.new("Part")
childPart.Size = Vector3.new(2, 2, 2)
childPart.Anchored = true
childPart.Parent = parentPart
childPart.Name = "Child"
-- Position the child part relative to the parent part using Local CFrame
local partCFrameLocal = CFrame.new(2, 2, 0) -- Local space offset
childPart.CFrame = parentPart.CFrame * partCFrameLocal -- Set the child part's CFrame
print("Child part created with Local Position:", partCFrameLocal.Position)
-- Print parent's world space position
print("Parent Part's World Position:", parentPart.CFrame.Position)
-- Demonstrating ToWorldSpace and ToObjectSpace
local modelCFrameWorld = parentPart.CFrame -- Parent's world CFrame
local partCFrameWorld = modelCFrameWorld:ToWorldSpace(partCFrameLocal)
print("World Position:", partCFrameWorld.Position) -- Prints the position of the part in world space
local recalculatedPartCFrameLocal = modelCFrameWorld:ToObjectSpace(partCFrameWorld)
print("Recalculated Local Position:", recalculatedPartCFrameLocal.Position) -- Should match partCFrameLocal.Position
end
-- Call the function to create the child part
createChildPart()Roblox Studio
Looking for more useful tools to boost your productivity?
Explore More ToolsIf you found this tutorial helpful and would like to support my work, please consider buying me a coffee.
Thank you very much for your support!
Buy me a coffee