Una coroutine es una herramienta de programación que te permite pausar y reanudar funciones en ciertos puntos. A diferencia de las funciones regulares que se ejecutan de manera continua, las coroutines se detienen en pausas designadas y continúan más tarde. Esta función es útil para gestionar tareas que necesitan ocurrir con el tiempo sin detener todo el programa.
| Descripción | |
|---|---|
| Yield | La operación utilizada dentro de una coroutine para pausar su ejecución, permitiendo que otro código se ejecute. Detiene temporalmente la coroutine y guarda su estado. |
| Resume | La operación que reinicia una coroutine desde el punto donde se pausó por última vez, continuando con su ejecución. |
| Status | Una función para verificar el estado actual de una coroutine, como si está suspendida, en ejecución, o terminada (completada). |
| Wrap | Una función envolvente que reanudará una coroutine particular cuando se llame y solo devolverá los valores suspendidos. |
Ejemplo: Coroutine
local function countingCoroutine()
for i = 1, 3 do -- Count from 1 to 3
coroutine.yield("Count: " .. i) -- Yield the count value
end
return "Counting completed." -- Return a final message when done
end
-- Create the coroutine from the function
local co = coroutine.create(countingCoroutine)
-- Start the coroutine and check the status and results at each step
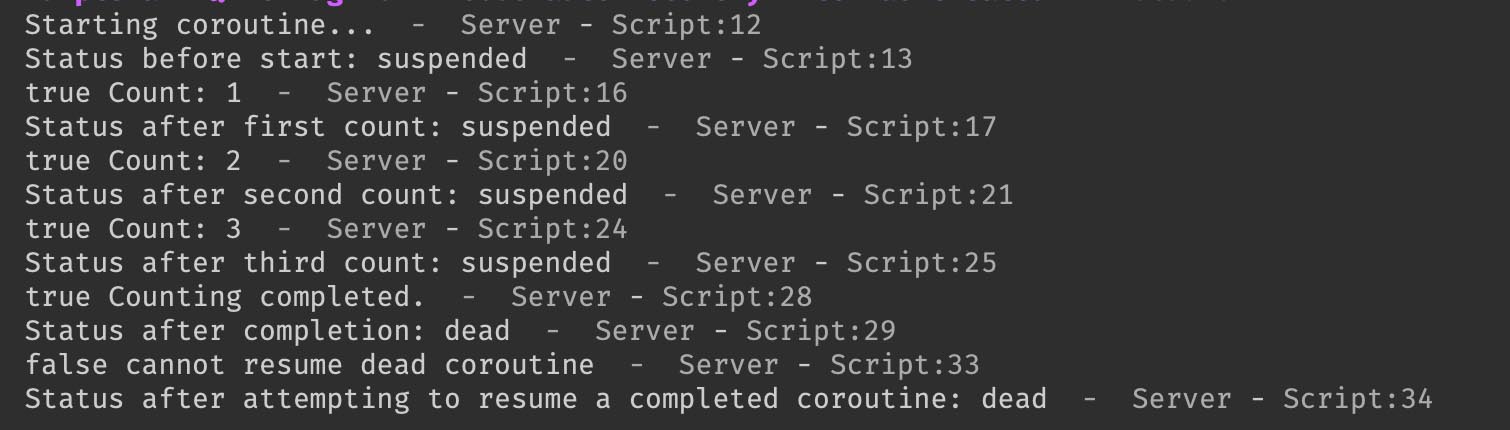
print("Starting coroutine...")
print("Status before start:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Initially, status should be 'suspended'
local success, result = coroutine.resume(co) -- Resume for the first count
print(success, result) -- Should print true, "Count: 1"
print("Status after first count:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should still be 'suspended'
success, result = coroutine.resume(co) -- Resume for the second count
print(success, result) -- Should print true, "Count: 2"
print("Status after second count:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should still be 'suspended'
success, result = coroutine.resume(co) -- Resume for the third count
print(success, result) -- Should print true, "Count: 3"
print("Status after third count:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should still be 'suspended'
success, result = coroutine.resume(co) -- Resume for the final return
print(success, result) -- Should print true, "Counting completed."
print("Status after completion:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should now be 'dead'
-- Check status after completion to confirm no further actions can be taken
success, result = coroutine.resume(co)
print(success, result) -- Should print false and possibly an error message
print("Status after attempting to resume a completed coroutine:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should be 'dead'Roblox Studio
Ejemplo: Usando coroutine.wrap
local function countToThree()
for i = 1, 3 do
coroutine.yield("Count: " .. i) -- Yield with a return value
end
return "Counting completed." -- Return a final message when done
end
local wrappedCoroutine = coroutine.wrap(countToThree)
print("Starting coroutine...")
local result
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- Executes and yields "Count: 1"
print(result) -- Prints "Count: 1"
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- Resumes and yields "Count: 2"
print(result) -- Prints "Count: 2"
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- Resumes and yields "Count: 3"
print(result) -- Prints "Count: 3"
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- Ends the counting, returns "Counting completed."
print(result) -- Prints "Counting completed."
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- ErrorRoblox Studio
¿Buscas más herramientas útiles para aumentar tu productividad?
Explorar Más HerramientasSi encuentras útil este tutorial y deseas apoyar mi trabajo, considera invitarme a un café.
¡Muchas gracias por tu apoyo!
Invítame a un café