Méthodes et Propriétés de l'Humanoïde
Empty
Empty
Empty
| TakeDamage | Réduit la santé de l'humanoïde de la quantité spécifiée. |
| MoveTo | Fait marcher l'humanoïde vers l'emplacement ou la pièce donnée. |
| GetState | Retourne l'état actuel de l'humanoïde en tant que Enum.HumanoidStateType. |
| ChangeState | Force l'humanoïde à passer à l'état spécifié. |
| RemoveAccessories | Retire tous les accessoires portés par le modèle parent de l'humanoïde. |
| ReplaceBodyPartR15 | Remplace une partie du corps R15 par une autre pièce. |
| SetStateEnabled | Active ou désactive l'état spécifié pour l'humanoïde. |
| UnequipTools | Déséquipe tous les outils actuellement équipés par l'humanoïde. |
| ApplyDescription | Applique une HumanoidDescription à l'humanoïde. |
| ApplyDescriptionReset | Applique une HumanoidDescription à l'humanoïde et réinitialise les modifications. |
| PlayEmote | Joue l'émote spécifiée si elle est valide. |
| Move | Fait bouger l'humanoïde dans la direction spécifiée. |
| GetMoveVelocity | Retourne la vitesse de déplacement actuelle de l'humanoïde. |
| EquipTool | Équipe l'outil spécifié à l'humanoïde. |
Empty
Empty
Empty
| Health | Représente la santé actuelle de l'humanoïde. |
| MaxHealth | Représente la santé maximale que l'humanoïde peut avoir. |
| WalkSpeed | Détermine la vitesse de marche de l'humanoïde. |
| JumpPower | Contrôle la puissance des sauts de l'humanoïde. |
| HipHeight | La hauteur des hanches de l'humanoïde au-dessus du sol. |
| AutoRotate | Détermine si l'humanoïde se tourne automatiquement pour faire face à sa direction de mouvement. |
| BreakJointsOnDeath | Contrôle si les articulations de l'humanoïde se cassent à sa mort. |
| CameraOffset | Le décalage de la caméra par rapport à l'humanoïde. |
| FloorMaterial | Indique le type de matériau du sol sur lequel se trouve l'humanoïde. |
| NameDisplayDistance | La distance à laquelle le nom de l'humanoïde est affiché. |
| NameOcclusion | Détermine comment la plaque nominative est affichée. |
| Sit | Indique si l'humanoïde est assis. |
| TargetPoint | Le point vers lequel l'humanoïde se déplace. |
Exemple de Santé de l'Humanoïde
Empty
Empty
Empty
local Players = game:GetService("Players")
local function onPlayerAdded(player)
-- Wait for the player's character to load
local character = player.Character or player.CharacterAdded:Wait()
local humanoid = character:WaitForChild("Humanoid")
-- Example: Setting Health
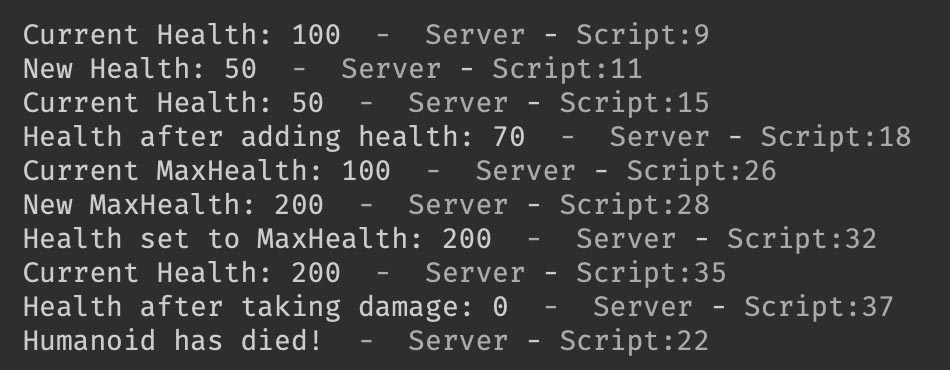
print("Current Health:", humanoid.Health)
humanoid.Health = 50 -- Set health to 50
print("New Health:", humanoid.Health)
-- Example: Adding Health
print("Current Health:", humanoid.Health)
local healthToAdd = 20
humanoid.Health = math.min(humanoid.Health + healthToAdd, humanoid.MaxHealth)
print("Health after adding health:", humanoid.Health)
-- Example: Checking if Humanoid is Dead
humanoid.Died:Connect(function()
print("Humanoid has died!")
end)
-- Example: Changing MaxHealth
print("Current MaxHealth:", humanoid.MaxHealth)
humanoid.MaxHealth = 200 -- Set MaxHealth to 200
print("New MaxHealth:", humanoid.MaxHealth)
-- Example: Setting Health to MaxHealth
humanoid.Health = humanoid.MaxHealth
print("Health set to MaxHealth:", humanoid.Health)
-- Example: Taking Damage
print("Current Health:", humanoid.Health)
humanoid.Health = humanoid.Health - 300 -- Directly reduce health by 300
print("Health after taking damage:", humanoid.Health)
end
-- Connect the function to the PlayerAdded event
Players.PlayerAdded:Connect(onPlayerAdded)Roblox Studio
Exemple d'Animation de l'Humanoïde
Empty
Empty
Empty
local Players = game:GetService("Players")
local UserInputService = game:GetService("UserInputService")
local player = Players.LocalPlayer
local character = player.Character or player.CharacterAdded:Wait()
local humanoid = character:WaitForChild("Humanoid")
-- Animation setup
local animation = Instance.new("Animation")
animation.AnimationId = "rbxassetid://131036267483527" -- Replace with your animation asset ID
-- Load the animation onto the humanoid
local animationTrack = humanoid:LoadAnimation(animation)
animationTrack.Looped = false -- Ensure the animation does not loop by default
-- Function to play the animation
local function playAnimation()
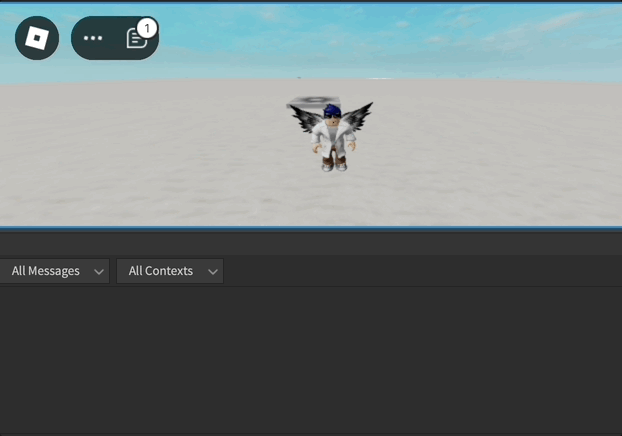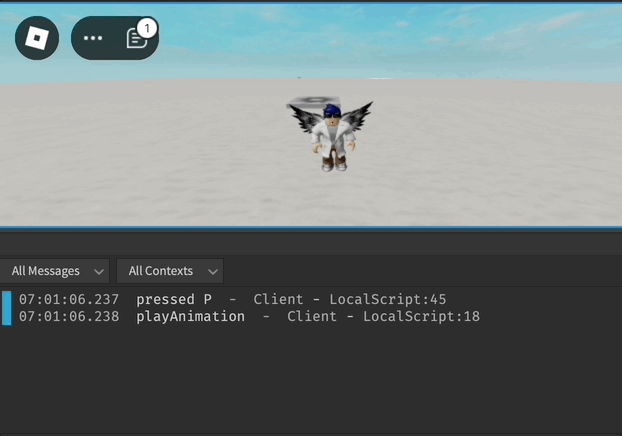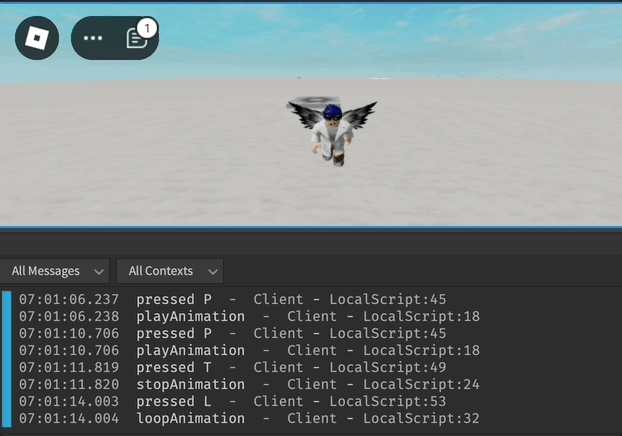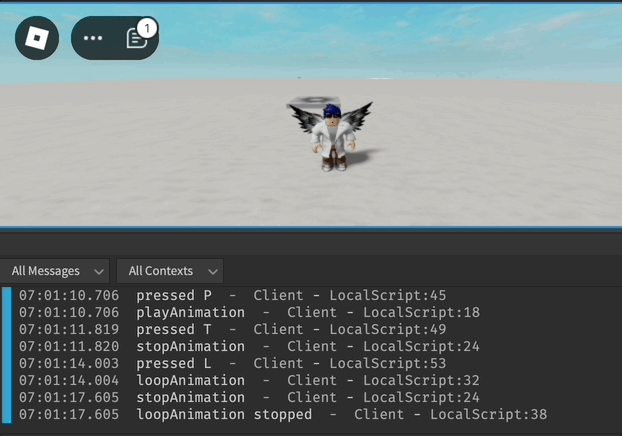
print("playAnimation")
animationTrack:Play()
end
-- Function to stop the animation
local function stopAnimation()
print("stopAnimation")
animationTrack:Stop()
end
-- Function to loop the animation
local function loopAnimation(loopCount)
animationTrack.Looped = true
animationTrack:Play()
print("loopAnimation")
-- Stop looping after the specified count
delay(loopCount * animationTrack.Length, function()
animationTrack.Looped = false
stopAnimation()
print("loopAnimation stopped")
end)
end
-- Detect when "P", "T", or "L" is pressed and trigger the appropriate function
UserInputService.InputBegan:Connect(function(input, gameProcessedEvent)
if input.KeyCode == Enum.KeyCode.P and not gameProcessedEvent then
print("pressed P")
playAnimation()
end
if input.KeyCode == Enum.KeyCode.T and not gameProcessedEvent then
print("pressed T")
stopAnimation()
end
if input.KeyCode == Enum.KeyCode.L and not gameProcessedEvent then
print("pressed L")
loopAnimation(3)
end
end)Roblox Studio
Exemple de Mouvement de l'Humanoïde
Empty
Empty
Empty
-- Function to make the humanoid walk to a specific point
local function walkToPoint(point)
humanoid:MoveTo(point)
end
-- Function to make the humanoid move in a specific direction
local function moveInDirection(direction)
humanoid:Move(direction)
end
-- Function to stop the humanoid's movement
local function stopMovement()
humanoid:Move(Vector3.new(0, 0, 0))
end
-- Example usage
local targetPoint = Vector3.new(10, 0, 10) -- Define a target point
walkToPoint(targetPoint) -- Make the humanoid walk to the target point
-- After a delay, make the humanoid move in a specific direction
wait(2)
local direction = Vector3.new(1, 0, 0) -- Define a direction
moveInDirection(direction)
-- After a delay, stop the humanoid's movement
wait(2)
stopMovement()Roblox Studio
Empty
Empty
Empty
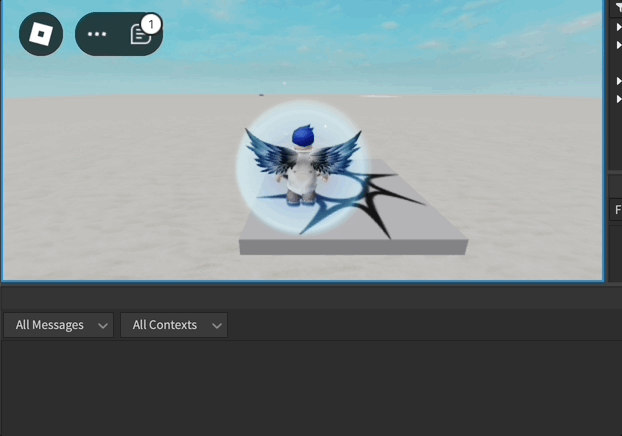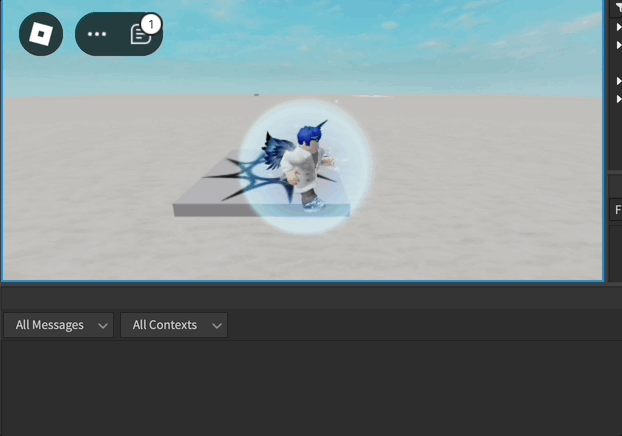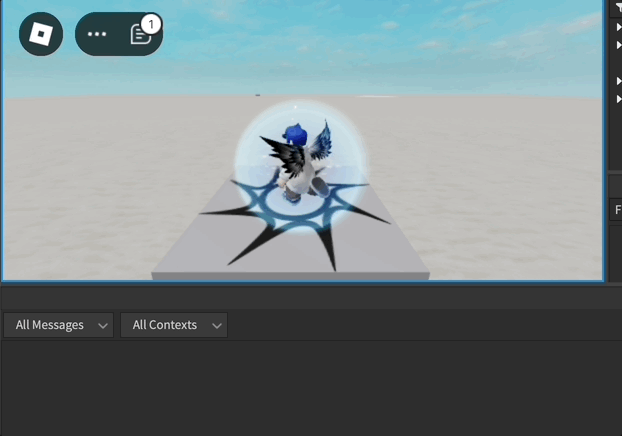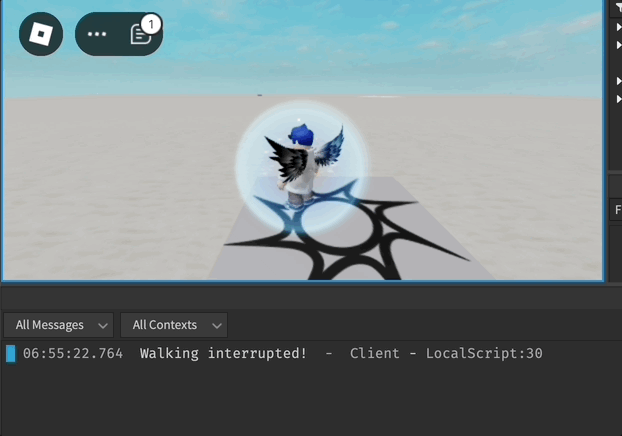
- Lors de l'utilisation de Humanoid:MoveTo, l'humanoïde joue automatiquement les animations de marche ou de course appropriées.
- Cette méthode définit l'état interne de l'humanoïde à Walking ou Running et le change en Idle une fois que la cible est atteinte ou si le mouvement est interrompu.
- L'événement MoveToFinished est déclenché lorsque l'humanoïde atteint la destination ou échoue à le faire dans un délai spécifié.
Exemple d'Événements de l'Humanoïde
Empty
Empty
Empty
local Players = game:GetService("Players")
local player = Players.LocalPlayer
local character = player.Character or player.CharacterAdded:Wait()
local humanoid = character:WaitForChild("Humanoid")
-- Function to handle when the humanoid finishes moving to a point
humanoid.MoveToFinished:Connect(function(reached)
if reached then
print("Humanoid reached the destination")
else
print("Humanoid did not reach the destination")
end
end)
-- Example function stubs for each event
local function onDied()
print("Humanoid died")
end
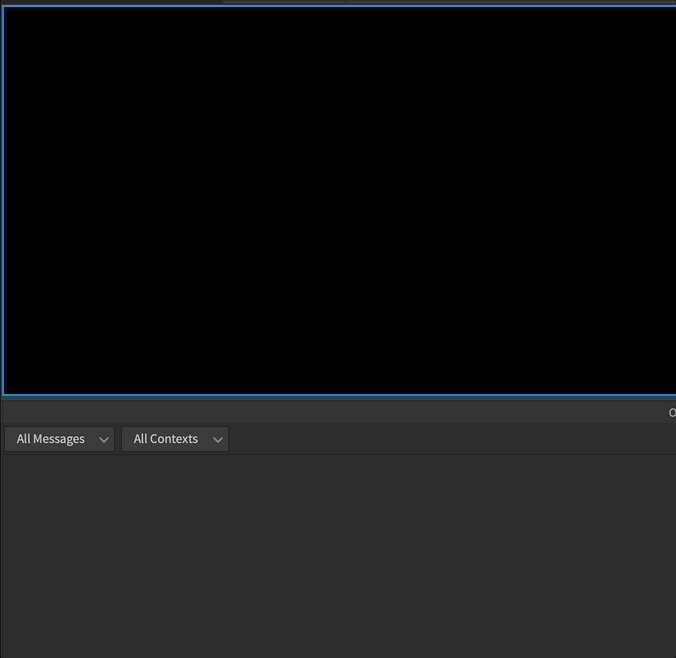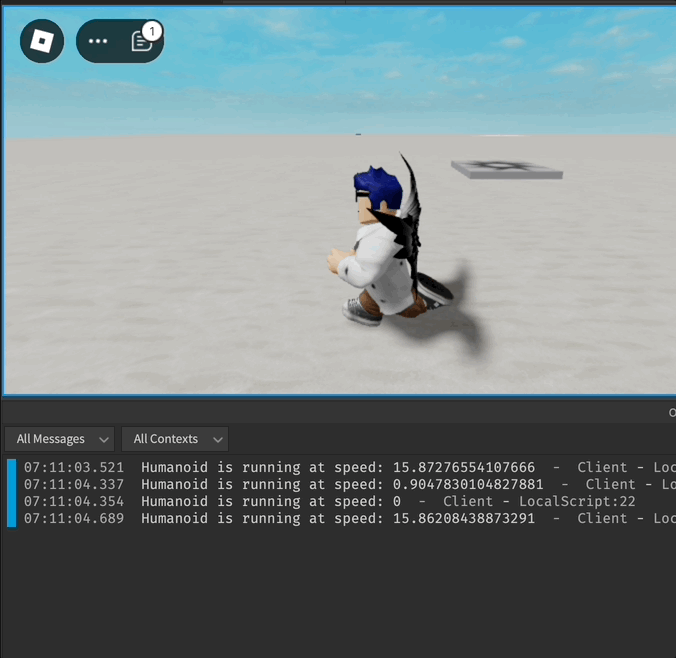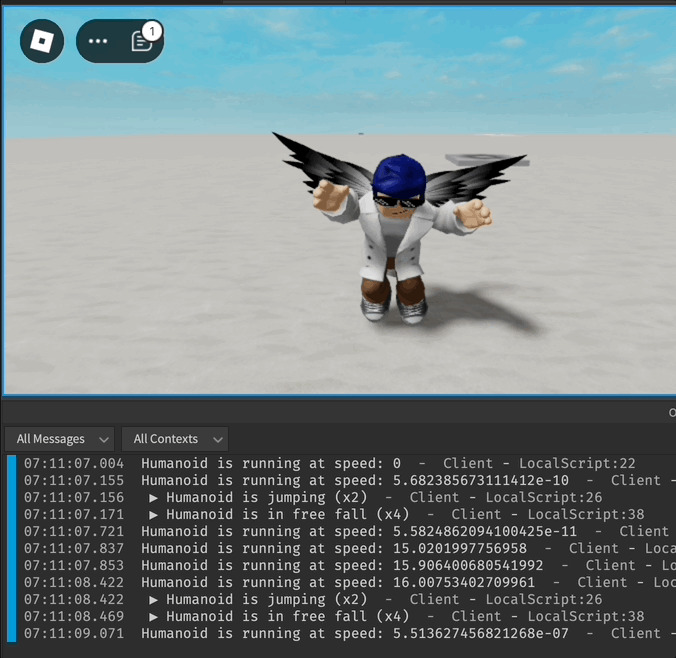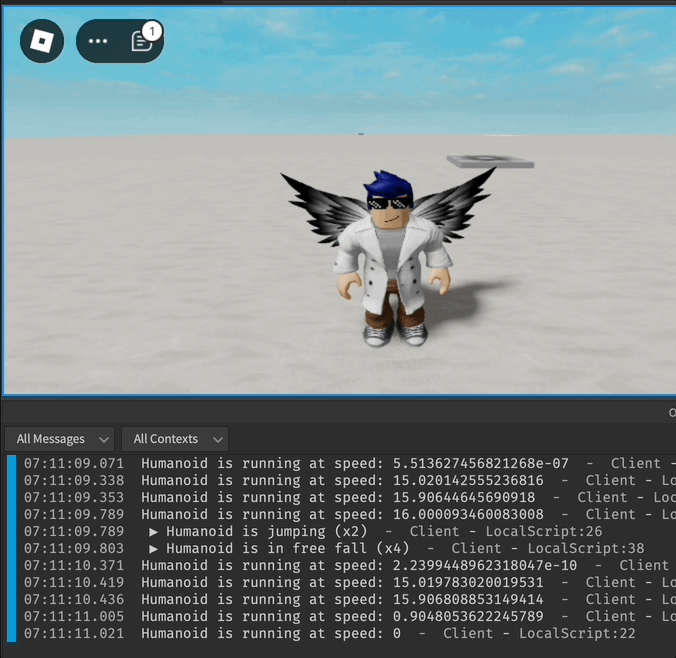
local function onRunning(speed)
print("Humanoid is running at speed:", speed)
end
local function onJumping()
print("Humanoid is jumping")
end
local function onClimbing()
print("Humanoid is climbing")
end
local function onGettingUp()
print("Humanoid is getting up")
end
local function onFreeFalling()
print("Humanoid is in free fall")
end
local function onFallingDown()
print("Humanoid is falling down")
end
local function onSeated()
print("Humanoid is seated")
end
local function onPlatformStanding()
print("Humanoid is platform standing")
end
local function onSwimming()
print("Humanoid is swimming")
end
-- Connect the functions to the respective humanoid events
humanoid.Died:Connect(onDied)
humanoid.Running:Connect(onRunning)
humanoid.Jumping:Connect(onJumping)
humanoid.Climbing:Connect(onClimbing)
humanoid.GettingUp:Connect(onGettingUp)
humanoid.FreeFalling:Connect(onFreeFalling)
humanoid.FallingDown:Connect(onFallingDown)
humanoid.Seated:Connect(onSeated)
humanoid.PlatformStanding:Connect(onPlatformStanding)
humanoid.Swimming:Connect(onSwimming)Roblox Studio
Vous cherchez plus d'outils utiles pour améliorer votre productivité ?
Découvrir Plus d'OutilsSi ce tutoriel vous a été utile et que vous souhaitez soutenir mon travail, veuillez envisager de m'offrir un café.
Merci beaucoup pour votre soutien !
M'offrir un café