Una coroutine è uno strumento di programmazione che consente di sospendere e riprendere l'esecuzione delle funzioni in punti specifici. A differenza delle funzioni normali che vengono eseguite dall'inizio alla fine, le coroutine si fermano in pause designate e continuano successivamente. Questa caratteristica è utile per gestire compiti che devono svolgersi nel tempo senza interrompere l'intero programma.
| Descrizione | |
|---|---|
| Yield | L'operazione utilizzata all'interno di una coroutine per sospendere la sua esecuzione, consentendo l'esecuzione di altri codici. Temporaneamente interrompe la coroutine e ne salva lo stato. |
| Resume | L'operazione che riavvia una coroutine dal punto in cui è stata interrotta l'ultima volta, continuando la sua esecuzione. |
| Status | Una funzione per controllare lo stato attuale di una coroutine, ad esempio se è sospesa, in esecuzione o terminata (completata). |
| Wrap | Una funzione di wrapping che riprende una particolare coroutine quando viene chiamata e restituisce solo i valori sospesi. |
Esempio: Coroutine
local function countingCoroutine()
for i = 1, 3 do -- Count from 1 to 3
coroutine.yield("Count: " .. i) -- Yield the count value
end
return "Counting completed." -- Return a final message when done
end
-- Create the coroutine from the function
local co = coroutine.create(countingCoroutine)
-- Start the coroutine and check the status and results at each step
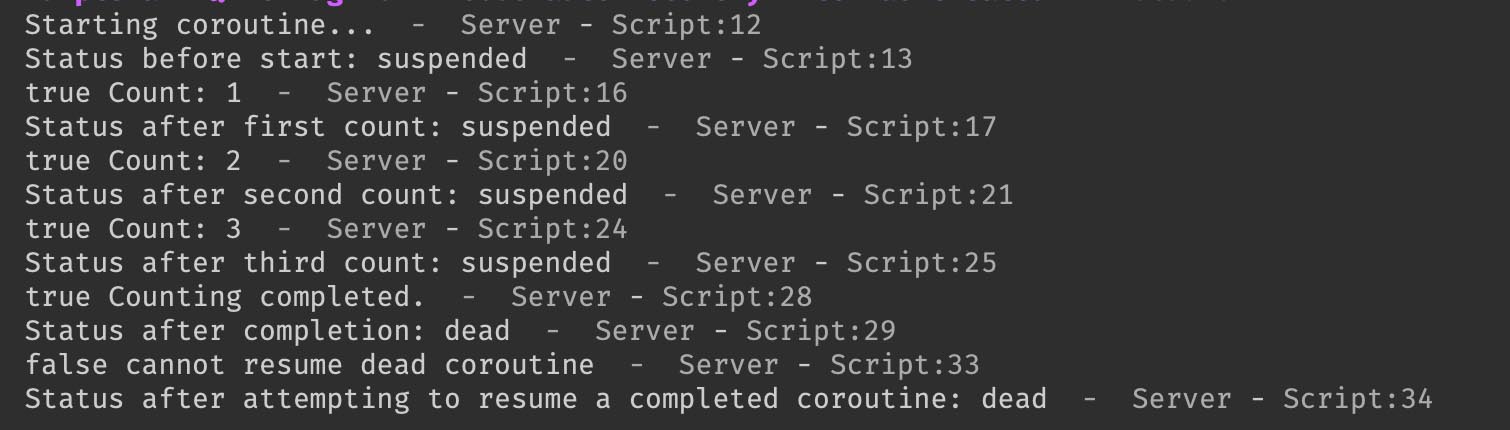
print("Starting coroutine...")
print("Status before start:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Initially, status should be 'suspended'
local success, result = coroutine.resume(co) -- Resume for the first count
print(success, result) -- Should print true, "Count: 1"
print("Status after first count:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should still be 'suspended'
success, result = coroutine.resume(co) -- Resume for the second count
print(success, result) -- Should print true, "Count: 2"
print("Status after second count:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should still be 'suspended'
success, result = coroutine.resume(co) -- Resume for the third count
print(success, result) -- Should print true, "Count: 3"
print("Status after third count:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should still be 'suspended'
success, result = coroutine.resume(co) -- Resume for the final return
print(success, result) -- Should print true, "Counting completed."
print("Status after completion:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should now be 'dead'
-- Check status after completion to confirm no further actions can be taken
success, result = coroutine.resume(co)
print(success, result) -- Should print false and possibly an error message
print("Status after attempting to resume a completed coroutine:", coroutine.status(co)) -- Should be 'dead'Roblox Studio
Esempio: Uso di coroutine.wrap
local function countToThree()
for i = 1, 3 do
coroutine.yield("Count: " .. i) -- Yield with a return value
end
return "Counting completed." -- Return a final message when done
end
local wrappedCoroutine = coroutine.wrap(countToThree)
print("Starting coroutine...")
local result
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- Executes and yields "Count: 1"
print(result) -- Prints "Count: 1"
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- Resumes and yields "Count: 2"
print(result) -- Prints "Count: 2"
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- Resumes and yields "Count: 3"
print(result) -- Prints "Count: 3"
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- Ends the counting, returns "Counting completed."
print(result) -- Prints "Counting completed."
result = wrappedCoroutine() -- ErrorRoblox Studio
Cerchi altri strumenti utili per aumentare la tua produttività?
Scopri Altri StrumentiSe hai trovato utile questo tutorial e desideri supportare il mio lavoro, considera di offrirmi un caffè.
Grazie mille per il tuo supporto!
Offrimi un caffè