Métodos e Propriedades do Humanoide
Empty
Empty
Empty
| TakeDamage | Reduz a saúde do humanoide pela quantidade especificada. |
| MoveTo | Faz o humanoide andar até o local ou parte especificada. |
| GetState | Retorna o estado atual do humanoide como um Enum.HumanoidStateType. |
| ChangeState | Força o humanoide a mudar para o estado especificado. |
| RemoveAccessories | Remove todos os acessórios usados pelo modelo pai do humanoide. |
| ReplaceBodyPartR15 | Substitui uma parte do corpo R15 por outra parte. |
| SetStateEnabled | Habilita ou desabilita o estado especificado para o humanoide. |
| UnequipTools | Desequipa qualquer ferramenta atualmente equipada pelo humanoide. |
| ApplyDescription | Aplica uma HumanoidDescription ao humanoide. |
| ApplyDescriptionReset | Aplica uma HumanoidDescription ao humanoide e redefine quaisquer alterações. |
| PlayEmote | Executa a animação especificada se for válida. |
| Move | Faz o humanoide se mover na direção especificada. |
| GetMoveVelocity | Retorna a velocidade de movimento atual do humanoide. |
| EquipTool | Equipe a ferramenta especificada no humanoide. |
Empty
Empty
Empty
| Health | Representa a saúde atual do humanoide. |
| MaxHealth | Representa a saúde máxima que o humanoide pode ter. |
| WalkSpeed | Determina a velocidade com que o humanoide pode andar. |
| JumpPower | Controla a força dos saltos do humanoide. |
| HipHeight | A altura dos quadris do humanoide acima do chão. |
| AutoRotate | Determina se o humanoide gira automaticamente para enfrentar a direção do movimento. |
| BreakJointsOnDeath | Controla se as juntas do humanoide se quebram quando ele morre. |
| CameraOffset | O deslocamento da câmera em relação ao humanoide. |
| FloorMaterial | Indica o tipo de material do piso em que o humanoide está. |
| NameDisplayDistance | A distância na qual o nome do humanoide é exibido. |
| NameOcclusion | Determina como a placa de identificação é exibida. |
| Sit | Indica se o humanoide está sentado. |
| TargetPoint | O ponto para o qual o humanoide está se movendo. |
Exemplo de Saúde do Humanoide
Empty
Empty
Empty
local Players = game:GetService("Players")
local function onPlayerAdded(player)
-- Wait for the player's character to load
local character = player.Character or player.CharacterAdded:Wait()
local humanoid = character:WaitForChild("Humanoid")
-- Example: Setting Health
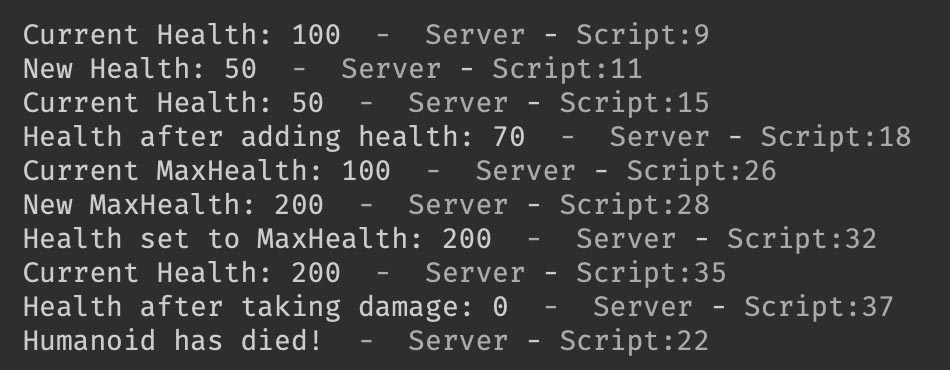
print("Current Health:", humanoid.Health)
humanoid.Health = 50 -- Set health to 50
print("New Health:", humanoid.Health)
-- Example: Adding Health
print("Current Health:", humanoid.Health)
local healthToAdd = 20
humanoid.Health = math.min(humanoid.Health + healthToAdd, humanoid.MaxHealth)
print("Health after adding health:", humanoid.Health)
-- Example: Checking if Humanoid is Dead
humanoid.Died:Connect(function()
print("Humanoid has died!")
end)
-- Example: Changing MaxHealth
print("Current MaxHealth:", humanoid.MaxHealth)
humanoid.MaxHealth = 200 -- Set MaxHealth to 200
print("New MaxHealth:", humanoid.MaxHealth)
-- Example: Setting Health to MaxHealth
humanoid.Health = humanoid.MaxHealth
print("Health set to MaxHealth:", humanoid.Health)
-- Example: Taking Damage
print("Current Health:", humanoid.Health)
humanoid.Health = humanoid.Health - 300 -- Directly reduce health by 300
print("Health after taking damage:", humanoid.Health)
end
-- Connect the function to the PlayerAdded event
Players.PlayerAdded:Connect(onPlayerAdded)Roblox Studio
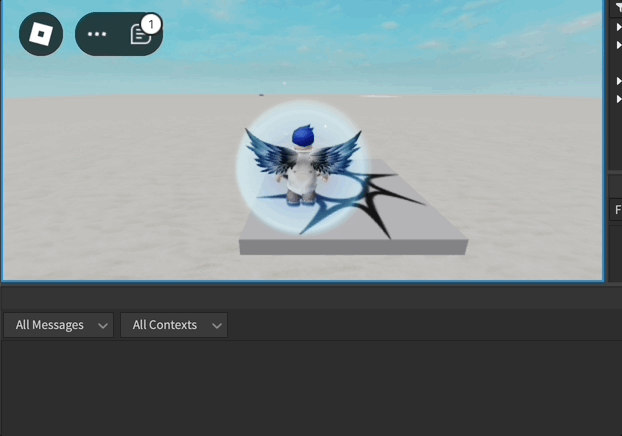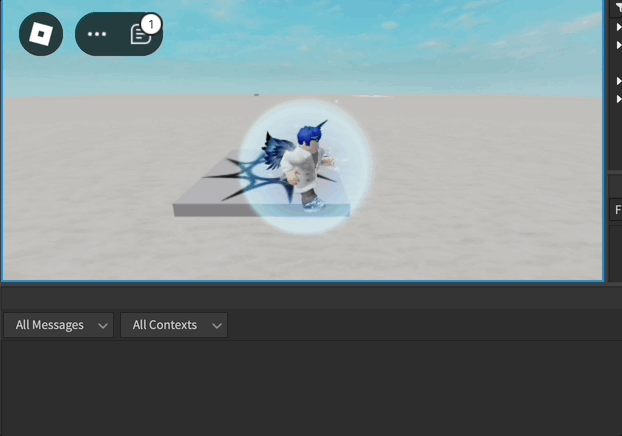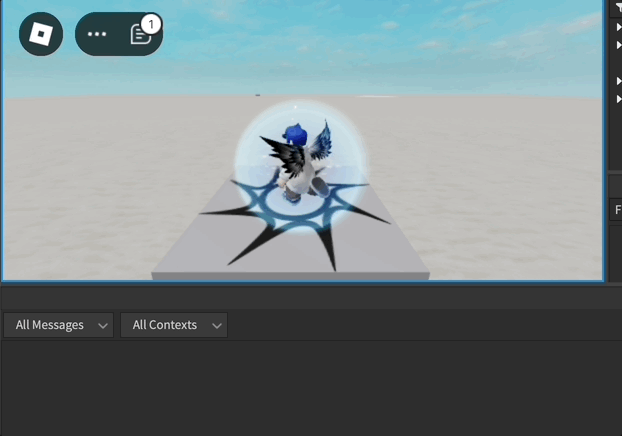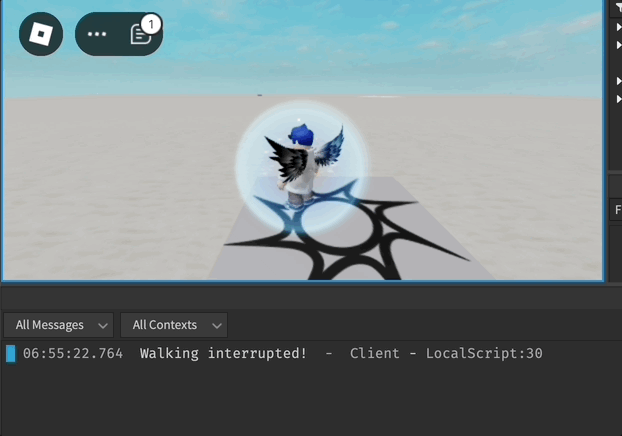
Exemplo de Animação do Humanoide
Empty
Empty
Empty
local Players = game:GetService("Players")
local UserInputService = game:GetService("UserInputService")
local player = Players.LocalPlayer
local character = player.Character or player.CharacterAdded:Wait()
local humanoid = character:WaitForChild("Humanoid")
-- Animation setup
local animation = Instance.new("Animation")
animation.AnimationId = "rbxassetid://131036267483527" -- Replace with your animation asset ID
-- Load the animation onto the humanoid
local animationTrack = humanoid:LoadAnimation(animation)
animationTrack.Looped = false -- Ensure the animation does not loop by default
-- Function to play the animation
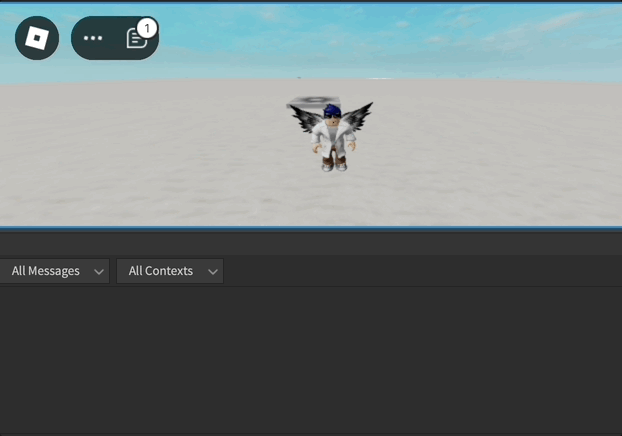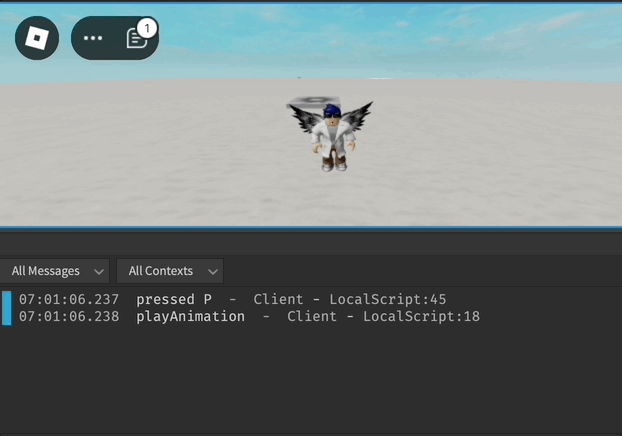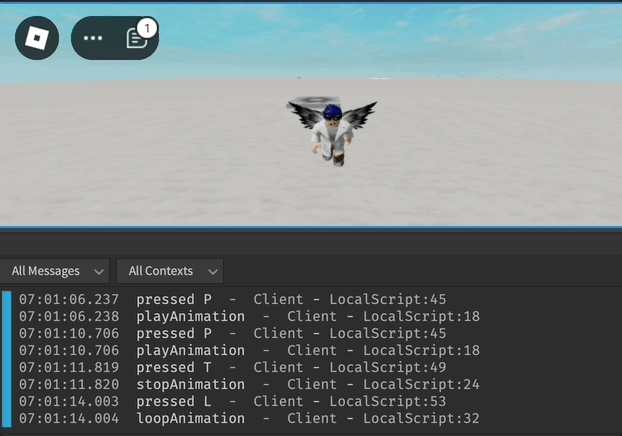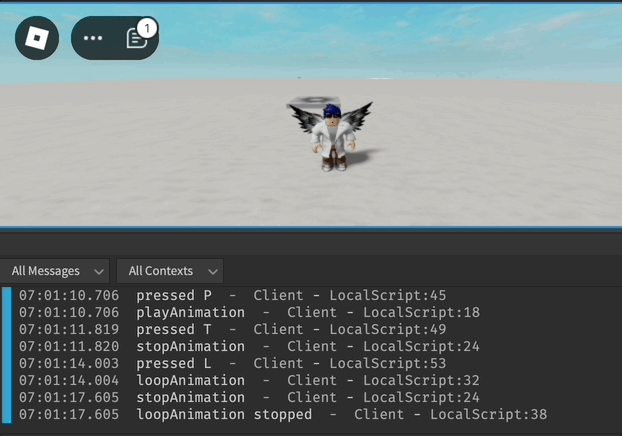
local function playAnimation()
print("playAnimation")
animationTrack:Play()
end
-- Function to stop the animation
local function stopAnimation()
print("stopAnimation")
animationTrack:Stop()
end
-- Function to loop the animation
local function loopAnimation(loopCount)
animationTrack.Looped = true
animationTrack:Play()
print("loopAnimation")
-- Stop looping after the specified count
delay(loopCount * animationTrack.Length, function()
animationTrack.Looped = false
stopAnimation()
print("loopAnimation stopped")
end)
end
-- Detect when "P", "T", or "L" is pressed and trigger the appropriate function
UserInputService.InputBegan:Connect(function(input, gameProcessedEvent)
if input.KeyCode == Enum.KeyCode.P and not gameProcessedEvent then
print("pressed P")
playAnimation()
end
if input.KeyCode == Enum.KeyCode.T and not gameProcessedEvent then
print("pressed T")
stopAnimation()
end
if input.KeyCode == Enum.KeyCode.L and not gameProcessedEvent then
print("pressed L")
loopAnimation(3)
end
end)Roblox Studio
Exemplo de Movimento do Humanoide
Empty
Empty
Empty
-- Function to make the humanoid walk to a specific point
local function walkToPoint(point)
humanoid:MoveTo(point)
end
-- Function to make the humanoid move in a specific direction
local function moveInDirection(direction)
humanoid:Move(direction)
end
-- Function to stop the humanoid's movement
local function stopMovement()
humanoid:Move(Vector3.new(0, 0, 0))
end
-- Example usage
local targetPoint = Vector3.new(10, 0, 10) -- Define a target point
walkToPoint(targetPoint) -- Make the humanoid walk to the target point
-- After a delay, make the humanoid move in a specific direction
wait(2)
local direction = Vector3.new(1, 0, 0) -- Define a direction
moveInDirection(direction)
-- After a delay, stop the humanoid's movement
wait(2)
stopMovement()Roblox Studio
Empty
Empty
Empty
- Ao usar Humanoid:MoveTo, o humanoide executa automaticamente as animações de caminhar ou correr apropriadas.
- Este método define o estado interno do humanoide como Caminhando ou Correndo e o altera de volta para Inativo assim que o alvo é atingido ou se o movimento for interrompido.
- O evento MoveToFinished é acionado quando o humanoide atinge o destino ou não consegue fazê-lo dentro de um período de tempo específico.
Exemplo de Eventos do Humanoide
Empty
Empty
Empty
local Players = game:GetService("Players")
local player = Players.LocalPlayer
local character = player.Character or player.CharacterAdded:Wait()
local humanoid = character:WaitForChild("Humanoid")
-- Function to handle when the humanoid finishes moving to a point
humanoid.MoveToFinished:Connect(function(reached)
if reached then
print("Humanoid reached the destination")
else
print("Humanoid did not reach the destination")
end
end)
-- Example function stubs for each event
local function onDied()
print("Humanoid died")
end
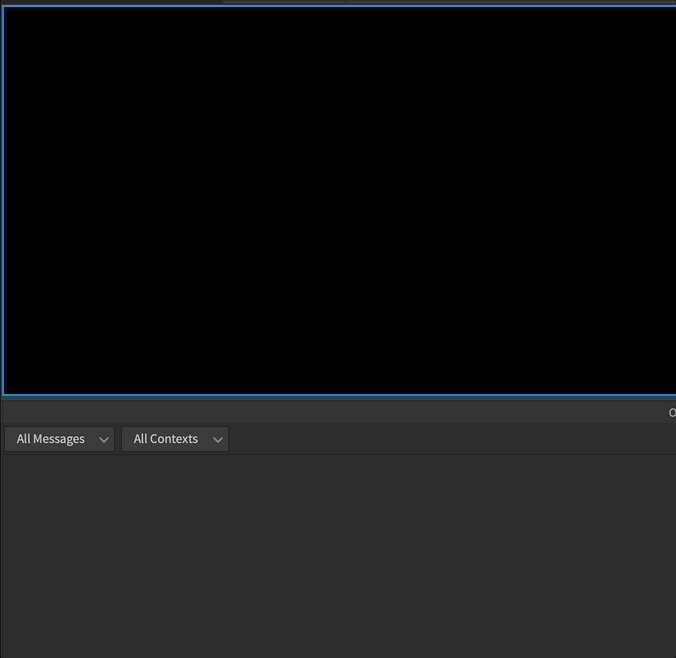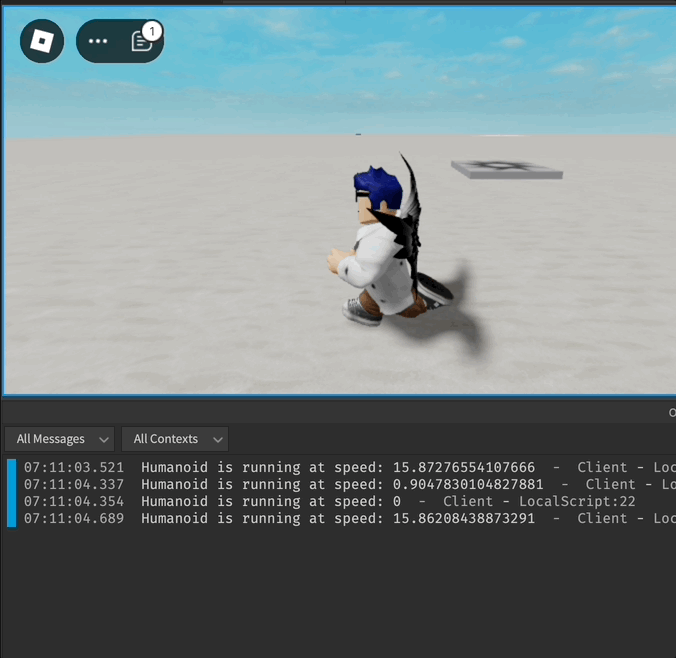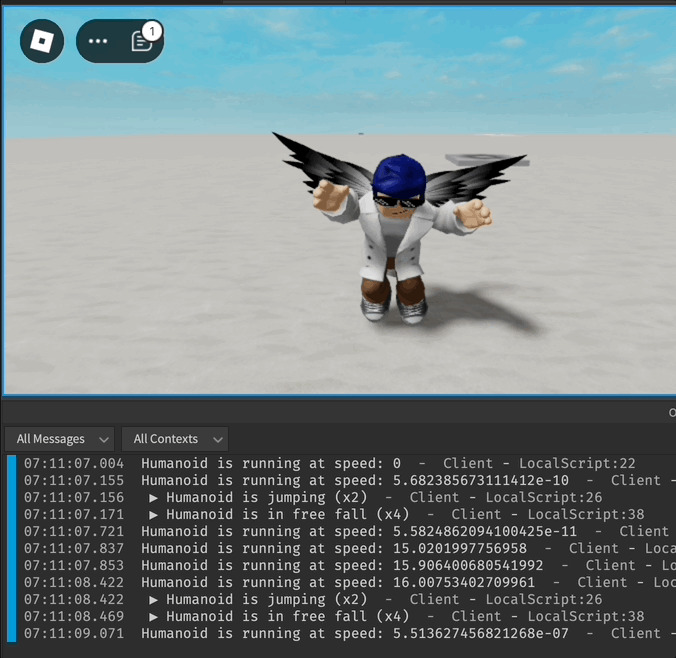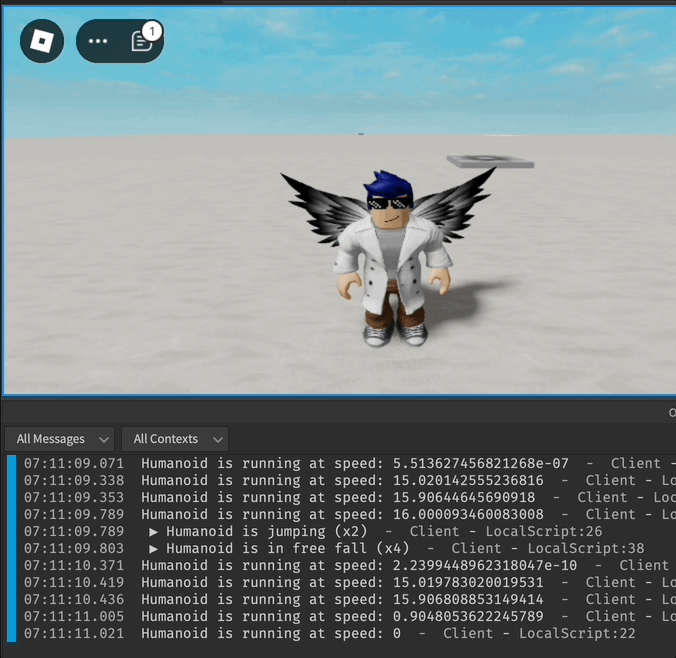
local function onRunning(speed)
print("Humanoid is running at speed:", speed)
end
local function onJumping()
print("Humanoid is jumping")
end
local function onClimbing()
print("Humanoid is climbing")
end
local function onGettingUp()
print("Humanoid is getting up")
end
local function onFreeFalling()
print("Humanoid is in free fall")
end
local function onFallingDown()
print("Humanoid is falling down")
end
local function onSeated()
print("Humanoid is seated")
end
local function onPlatformStanding()
print("Humanoid is platform standing")
end
local function onSwimming()
print("Humanoid is swimming")
end
-- Connect the functions to the respective humanoid events
humanoid.Died:Connect(onDied)
humanoid.Running:Connect(onRunning)
humanoid.Jumping:Connect(onJumping)
humanoid.Climbing:Connect(onClimbing)
humanoid.GettingUp:Connect(onGettingUp)
humanoid.FreeFalling:Connect(onFreeFalling)
humanoid.FallingDown:Connect(onFallingDown)
humanoid.Seated:Connect(onSeated)
humanoid.PlatformStanding:Connect(onPlatformStanding)
humanoid.Swimming:Connect(onSwimming)Roblox Studio
Procurando mais ferramentas úteis para aumentar sua produtividade?
Explorar Mais FerramentasSe você achou este tutorial útil e gostaria de apoiar meu trabalho, por favor, considere me comprar um café.
Muito obrigado pelo seu apoio!
Me compre um café